Hosts Files
They were used to translate domain names to IP addresses in earlier days of the internet but they are not used anymore.
A Hosts File is a text file containing domain names with IP addresses.
Locations:
Linux: /etc/hosts
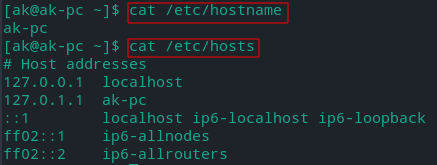
Windows: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
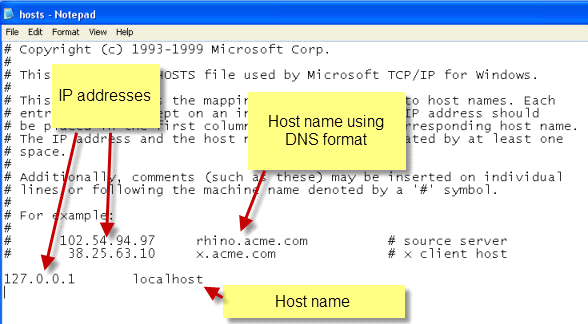
Hosts file are used to:
- Block websites (like ad websites)
- Redirect a website (hijacking attacks)
- Prevent malicious attacks or for content filtering
Tip: To prevent hijacking attacks change permission of hosts file to read only.
DNS - Behind The Scenes
Today DNS does not rely upon one file or one server, but instead upon many files across many servers around the globe. These servers are organized in a hierarchical manner.
Due to this distributed nature, the DNS system is resistant to outages (temporary suspension) of one or many of these servers.
DNS servers involved in loading a webpage:
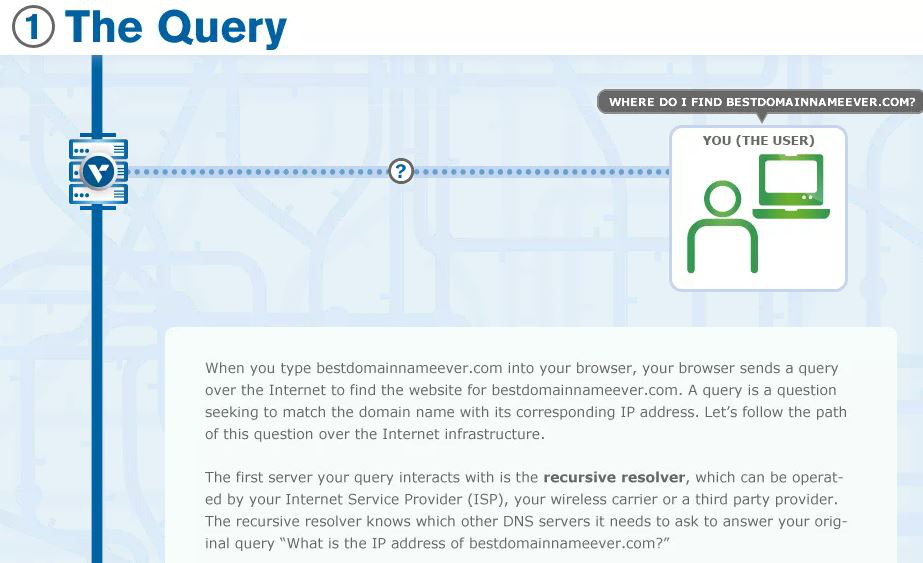
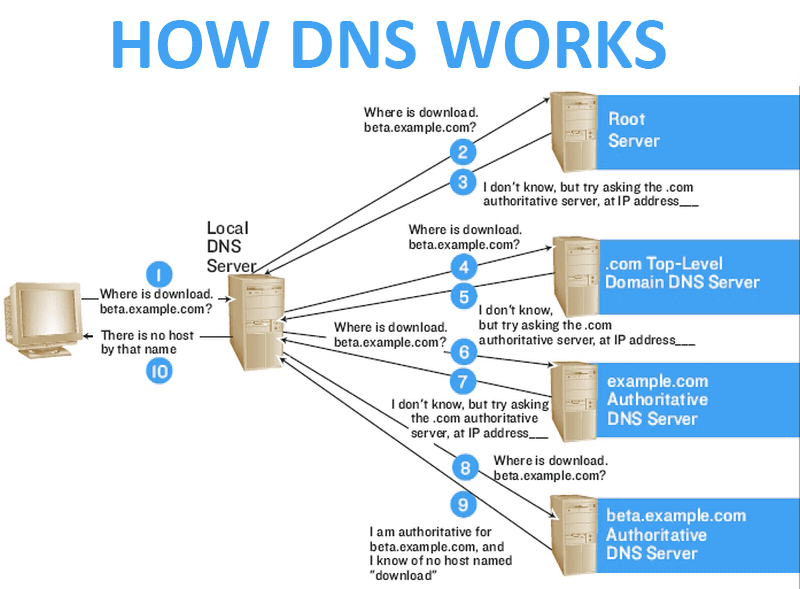
- DNS recursor (cache and forward resolver)) [Recursive = repeating process] - server designed to receive queries from client machines through applications such as web browsers and it also makes additional requests.
- Usually, the device is auto-configured to accept the network settings with the resolver being set to one under the control of the ISP.
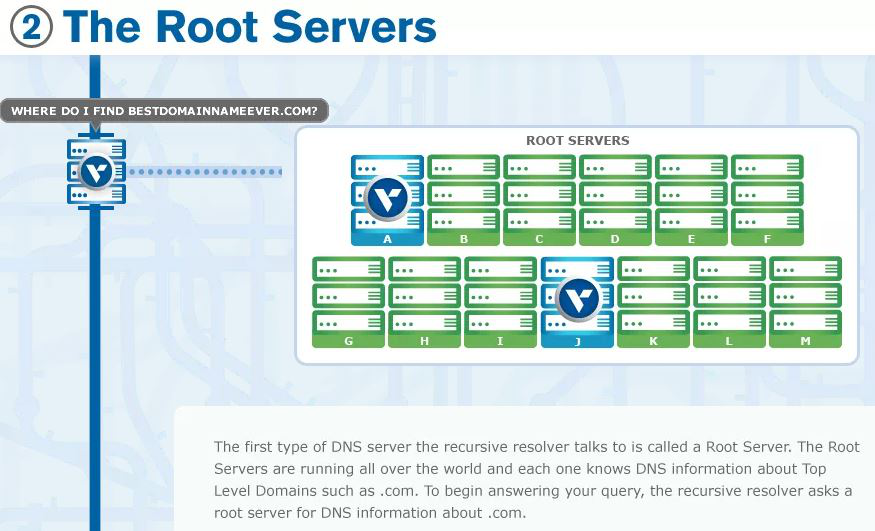
- Root nameserver - provides reference to other more specific locations.
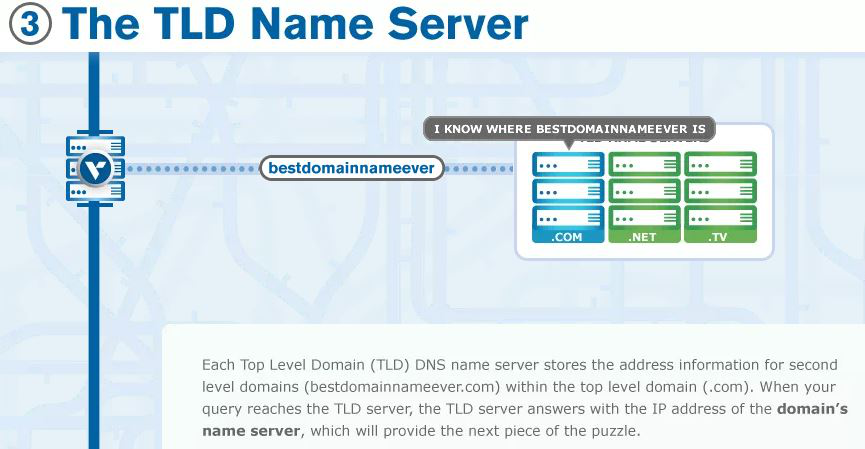
- TLD nameserver - it hosts the last portion of a hostname (In example.com, the TLD server host “com”).
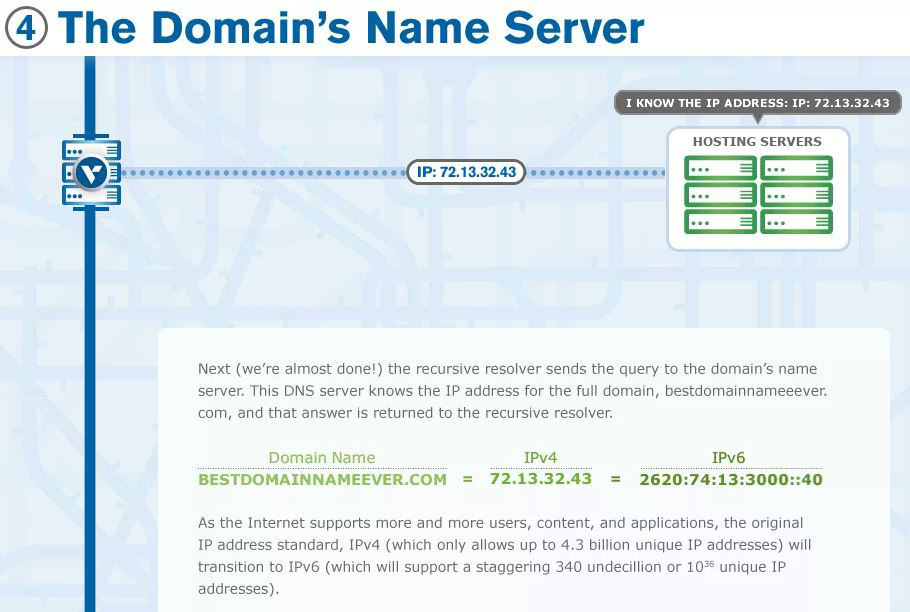
- Authoritative nameserver - It’s like a dictionary in which a specific name can be translated into it’s definition (address).
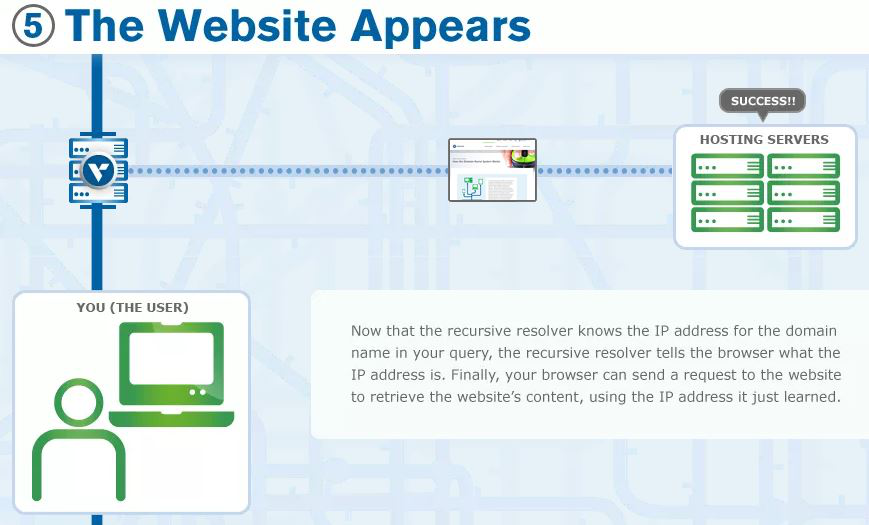
- If the authoritative name server has access to the requested record, it will return the IP address for the requested hostname back to the DNS Recursor that made the initial request.
- The resolver then responds to the client with the IP address of the domain requested initially and then client makes connection to the IP address.
- A "resolver" is the overall subsystem that does query resolution.
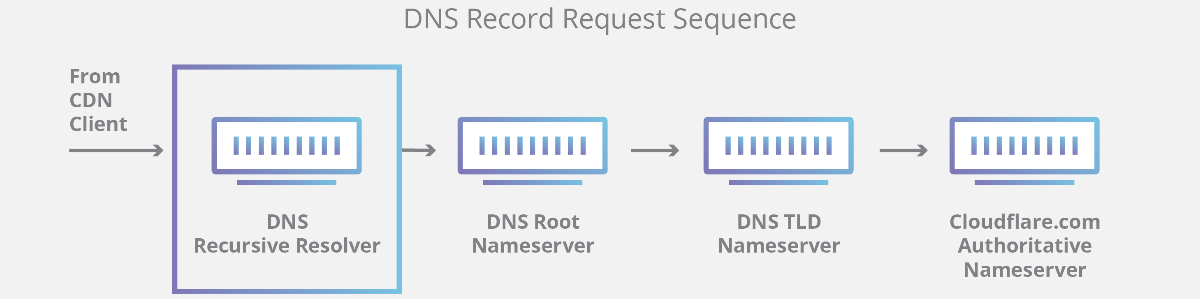
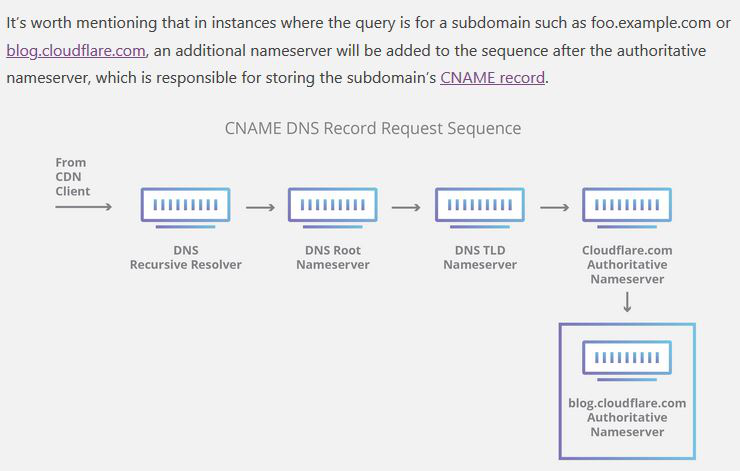
Working


Stub Resolver
It is a resolver present in the Operating System which just forward queries.
It is a component of the DNS that is accessed by application programs when using the DNS for e.g. resolving domain names to IP addresses.
The stub resolver simply serves as an intermediary between the application requiring DNS resolution, and a recursive DNS resolver.